Surface water, groundwater
Although, being two separate entities, surface- and groundwater are part of an interrelated system, the global water cycle (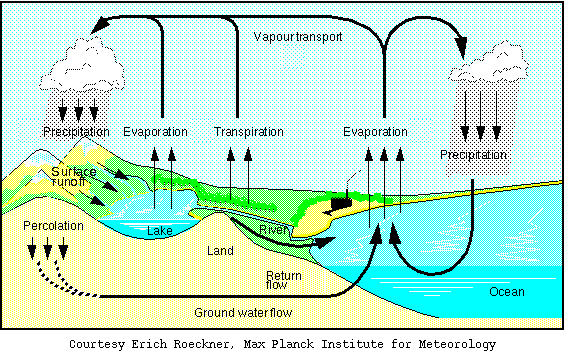 ). When surface water seeps through the soil it becomes groundwater and conversely, surface water sources can also be fed by groundwater.
). When surface water seeps through the soil it becomes groundwater and conversely, surface water sources can also be fed by groundwater.
Serving most of life's needs surface water makes up only around 1.2% of the total freshwater amount (being only 2.5% of all earth's water). Groundwater makes up around 30.1% of all freshwater. The following figure (left on the page) illustrates the composition in percentages of the total global water.
data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAHEAAAA0CAIAAAAyiUBYAAABwElEQVR4nO3YTXKEIBQEYI7mgVznJlbu4jL38CxkMcgIPBCwEaW6i40zCern42dUP79/bNimul/BeI2mjU01Uxua4kNTfGiKD03xoSk+NMWHpvjQFB+a4kNTfGiKD03xaWXa+Nlsy6SUUmpatjYnuJImpuErr5pe1lkJmVfnu8/hs3KTaUWfeymKpqPUaUyqouVc2aPZksk1BYJmyiZNhS/Fup6WTfpj7xNzOK92TvlOKe4MlDXV9DRNyxaZRiaKMtPATpzRz8dNf9PYGUtMzc17RHtRlZgeCnEXtf/m9/sCU++kcumZ+3FRzJF/834Rn5setdznVII6hCmqTo9WsdnEd362qXfGy/OpFYKbvqFOxSurmE8jlVRlKo39zPQ0TV9Zgam5/Wj5eKvN9wmkTG2hBjMqao3Sz9rzi2tUfITKP3PTpvHhDzTNzxVKm5Kxn9yefnJgndf9MG0q9Zyz6b/J9EpvpxFIwt9DN6aJqW7+rs9JuJqIG87b0sr0zkS3PZ1ev4xgqrWwCnV8sTqK6ZNCU3xoig9N8aEpPjTFh6b40BQfmuJDU3xoig9N8aEpPjTFJ2rKBmk0pekbGk3x7R9Ifh6gyNiEQQAAAABJRU5ErkJggg== The Earth's Water (http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/earthwherewater.html,accessed 2013-11-06)
Surface water
General Aspects
Surface water is any type of natural water on ground level that is, compared to groundwater, naturally open to atmosphere such as e.g. rivers, lakes, seas, wetlands, streams, and oceans.
Sources of surface water are:
precipitation
recruitment of groundwater
Losses can be:
evaporation (vaporization from the surface)
absorption by plants
seepage into the ground
abstraction by mankind for e.g. agriculture, industry, living</font
Global distribution of surface water
Throughout the globe surface water is naturally distributed in varying amounts since it is affected by precipitation, evaporation and runoff.
Precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapour that falls under gravity. This can be drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, graupel and hail, as main forms.[1]
Evaporation is the vaporation of water from land or from the water surface. [2]
When the soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess the water from rain, meltwater or other sources flows over the land, that is called runoff. [3]
data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAHEAAAA0CAIAAAAyiUBYAAABwElEQVR4nO3YTXKEIBQEYI7mgVznJlbu4jL38CxkMcgIPBCwEaW6i40zCern42dUP79/bNimul/BeI2mjU01Uxua4kNTfGiKD03xoSk+NMWHpvjQFB+a4kNTfGiKD03xaWXa+Nlsy6SUUmpatjYnuJImpuErr5pe1lkJmVfnu8/hs3KTaUWfeymKpqPUaUyqouVc2aPZksk1BYJmyiZNhS/Fup6WTfpj7xNzOK92TvlOKe4MlDXV9DRNyxaZRiaKMtPATpzRz8dNf9PYGUtMzc17RHtRlZgeCnEXtf/m9/sCU++kcumZ+3FRzJF/834Rn5setdznVII6hCmqTo9WsdnEd362qXfGy/OpFYKbvqFOxSurmE8jlVRlKo39zPQ0TV9Zgam5/Wj5eKvN9wmkTG2hBjMqao3Sz9rzi2tUfITKP3PTpvHhDzTNzxVKm5Kxn9yefnJgndf9MG0q9Zyz6b/J9EpvpxFIwt9DN6aJqW7+rs9JuJqIG87b0sr0zkS3PZ1ev4xgqrWwCnV8sTqK6ZNCU3xoig9N8aEpPjTFh6b40BQfmuJDU3xoig9N8aEpPjTFJ2rKBmk0pekbGk3x7R9Ifh6gyNiEQQAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==The World's Surface Water (http://www.grida.no/graphicslib/detail/worlds-surface-water-precipitation-evaporation-and-runoff_4701, accessed 2013-11-06)
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found