Human beings and the natural world are on a collision route. Human use the natural resources like water, land, air, etc. And human-made water pollution and water - waste is nasty, and disgust from the nature point of view. People consume foods and defecate using flushing toilet with heavy amount of water and it makes groundwater pollution as well as somehow happening dangerous disease to our human society. In the world, 2000 million people don’t have toilet (Deora 2004).The vicious cycles of human environmental processes are crucial to understand. There is some innovative solution in this discourse and is a sustainable way. Waterless (or dry) composting toilets have less water utilization and divert pollutant loads from the sewerage system direct to agriculture (Morgen 2007).
Introduction to the concept
Human nutrient cycle is an endless natural cycle. Ecosystems and their species provide a range of important goods and services for human society. These include water, food, cultural and other values (World Bank Report 2012). Human consume foods and defecate to the toilet is the natural process. Poor people in the developing countries usually defecate with flushing toilet. Flushing toilets use a heavy amount of water. For example, the amount of water usage in America is 188 gallons per person per day (Joseph 2005). In general, a family with a water flush toilet would use at least 100,000 litres of water a year for flushing (1). But, waterless composting toilets can reduce household water consumption by 40,000 gallons (151,423 liters) per year (2).
Many people in poor countries defecate on the ground or bushes without proper management, happened ground water or surface water pollutions as well as a series of problems, water-borne diseases like diarrhea, bacterial and amoebic dysentery, typhoid, cholera, and eutrophication. It can reduce the risk of human infection to acceptable levels without contaminating the environment or negatively affecting the life of its inhabitants (Environmental Protection Agency 1999).
Efficient waste management technique, no -groundwater pollution and sustainable innovative solution for agricultural purposes is coming out by shooting two birds in one stroke. This is called “Dry composting Toilet”. Dry composting toilet or urine separation toilet has several advantages. It has
• Less or no water use for flushing
• More affordable than sewerage systems
• Manageable at household level and thus put less pressure on municipal resources
• Less (or no) smell release than drop-and-store alternatives
• Accessible urine which contains most of the nutrients in the excreta
• Capacity to turn waste into a useful resource i.e. fertilizer
(Morgen 2007, Drangert 1998).
Developing country and its sustainable solution
In the green revolution age, human produced intensively a lot of foods, from nature, soil, and water. And, increasing use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, intensive agriculture makes the soil into nutrient depletion, soil structure deterioration, and of less healthy soil. The nature system is almost ruined out. Industrial age again, by human make cloud of CO2 into the air. And, its consequence problems such as ozone depletion, increasing global temperature, water deficit or drought, flooding, precipitation reduction or erratic rainfall, and the whole processes of climate change. The chance to avert the threats we now confront will be lost in no more than one or a few decades and the prospects for humanity immeasurably diminished (1,600 Senior Scientists 1992). Our world is almost destroyed and seldom reached point of no-return or no-recovery. All the processes was happened by human. New paradigms for socio-technological progress are needed towards sustainable futures, providing economic, organizational, legal and other societal aspects (VITO 2012).
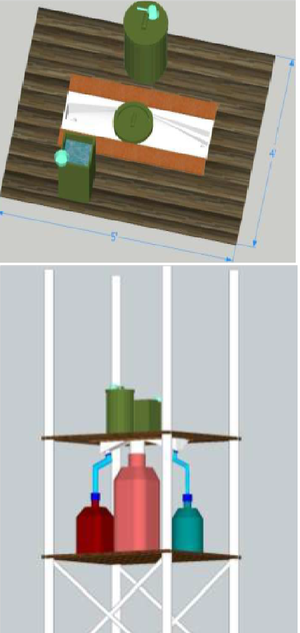
Fig. General Structure of Dry Composting Toilet
In the world, population outbreaks- reached about 7 billions and future projection for the world population is expected to reach 9 billion in 2050 (Lutz and Samir 2010).We need more foods to feed enough to the world entire population. We face the processes like energy crisis, financial crisis, and natural resources depletion, climate change, endangered biodiversity, inequality of wealth, and persisting greediness are considered as symptoms of the un-stainable world. Land is within bounce foods versus bio-energy. Water resources are becoming depleted, and water pollution makes double burden to have safe drinking water. In a water-scarce country like South Africa and many developing countries, sanitation options are needed to minimize the demand on water resources (Schutte and Pretorius 1997). Sustainable agriculture, organic farming, healthy soil and clean water for future generation, safe foods to sustain a life healthy, hygiene and perfect life to serve as a human is our sustainable world. “Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”(UN-WECD 1987).
Low cost-efficient solution to water sanitation
Typical septic tank or a pit latrine tends to pollute ground water and finally cause environmentally unsatisfactory. Area wide underground sewerage system with treatment facilities are costly to implement. Socially acceptable solution for human health, hygiene, no additional water for flushing, less (or no ) smell than drop and store alternative one, clean environment, no water pollution at all or no eutrophication, is the dry composting toilet with low cost-efficient solution for poor people in developing countries. It protects surface and ground water from sewage pollution as well as it would be avoided about 19% of an average household water usage and 28% of domestic sewage discharge by eliminating toilet flushing (GDH 2003).Dry composting toilets collect human waste and converts into a fertilizer resource for plant growth (3).
It is a feasible solution for developing countries because it has low cost, easy to do, and high community’s perceptions and environmental sustainable way and socially reliable option. The human excreta is high in nutrient value, and can use as a compost in agriculture for more production. After 6 months, the urine become like pure water that could utilize for agricultural water sources (Abraham et al, 2011, Morgen 2007).
Examples of water sanitation in developing countries
Economically viable, ecologically sound and environmentally sustainable way of human waste management and water sanitation is the dry composting toilet. It is now practically utilizing in all around the world. For example, US, EU, East Asia, South Asia, South Africa, and many developing countries are practicing this techniques for efficient human waste management and water sanitation option (e.g Sweden 30000 units, China 5 million units, etc) (Drangert 1998).
Improving water sanitation and socially efficient composting toilet in Inle lake, Myanmar
Clean, shallow and fresh water lake with 22 km long, average 3 m deep and 11 km wide Inle Lake is the major tourist attraction of Myanmar (approximately over 30,000 per year) as well the main water resources for the livelihoods of 36 floating villages, with 173,099 people (Soe 2012). The Inle Lake was assigned as an ASEAN Heritage Park and also is home to wetland species such as migratory and residential birds. The main livelihoods of the areas are floating gardening (like Hydroponic agriculture) and fishing. Water pollution has decreased the fisherman’ catch and thus, threats the livelihoods of the Inle region. The water quality is annually reduced due to the several combined effect, such as upland intensive agriculture around the lake, floating houses with hanging toilets, households activities like washing, bathing, cleaning, etc are relying on lake water. Eutrophication is becoming a prominent problem, loss of biodiversity of fishes and other aquatic animals (Swe 2011). The important item for the livelihoods of this region is the drinking water. Village communities tried to build a few water tanks in some collection point, but fetching water for the people is a routine work and time-consuming. Even the communities can control water pollution that happened by agriculture systems, they can’t afford to control water pollution made by human. People usually defecate directly to the lake water, and thus, contaminating the lake water with water borne diseases.
Dry composting toilet system can be afforded by all people around the lake and is also easy to practice. The compost toilet is a highly effective solution to sanitation in high water table and waterlogged areas (4').Urine and excreta are separately collected in the containers. Containers are separately used for excreta, urine and wash water. Several raw materials for drying materials like saw dust, rice husk, etc can use in the container. After the container is full, the human excreta can be applied as the organic nutrients for agriculture farms. Thus, the dry composting toilet will definitely improve local drinking water quality and thus reduce Diarrhea problems due to the eutrophication (Swe 2011).
Low cost, sanitary toilet that make compost for crops in Africa countries, Bangladesh and India context
Most of rural population in developing countries, like Africa, India, and Bangladesh, etc do not have access to safe and reliable toilet. There are several reasons of lacking toilet. Access to assets, lack of efficiency like money, poor knowledge, lack of education and health caring system, and poor technology are the major criteria of lacking toilet in developing countries. Due to the lack of toilet, the water born and air-borne diseases make double burden for their food security and poverty. There is an urgent need for the construction of simple, low-cost, affordable toilets that are easy to build and maintain and are relatively free of odors and flies. (Morgen 2007). The innovative solution is urine separation toilet, that is low cost, socially and moral acceptable, environmentally benefit. The unique features of the urine and excreta separation toilet are less water utilization, easy to practice and efficient compost from the excreta for agricultural purposes. After brown organic substances are turning into golden compost, the compost can directly use as an organic fertilizer for agricultural purposes.
Many successful stories of this innovative way of unique dry composting toilet and excellent environmental friendly ways of compost-making toilet for agricultural purposes have occurred in different regions of the world. The dry composting-sanitary projects have already laid down in Keyna, Zimbabwe, Malawi, South Africa, Bangladesh, India and many Africa countries ( 5, 6 Morgen 2007, Abraham et al.2011). The development of this innovation solution needs several processes, such as willingness to do, community involvement for sustainable ways, and government supports, etc.
When we looked back our past, our landscape level and our world almost ruined out or reached point of no return. Our regime is poor living standard and struggles with food security and health related problems in developing countries. The novelty, innovative solution created for developing countries in the transition world is socially acceptable, innovation technology like “Dry composting toilet”. Why Not?
Reference
Abraham, B, Kakumbi , G. M, Md. Monirul Alam & E. von Muench 2011.“Alternative Solutions for Challenging Environments: A look at UNICEF-assisted ecosan projects worldwide”, 35th WEDC International Conference, Loughborough, UK, 2011
Deora, A. 2004.“Appropriate Toilets for Developing Countries”, D-lab, Toilet Talk, RPCV-Jamica, Fall 2004.
EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency), 1999. “ Water Efficiency Technology Fact Sheet, Composting Toilets”, EPA 832-F-99-066, September 1999.
GHD, 2003. “Composting Toilet Demonstration”, Feasibility Study, Volume 1: Report, GHD in association with Demaine Partnership, Bensons Property Group and Environment Equipment, Smart Water Fund, December, 2003.
Ikuko Okamoto, 2012. “Decreasing Fish Resources: Case Study of Fisherman in Lake Inle, Myanmar”, Institute of Developing Economics, IDE discussion paper NO. 329, March, 2012.
Drangert, J. 1998. “Fighting the Urine Blindness to Provide more sanitation options”, Institute of Water and Environmental Studies, Linkoping University, 581 83 Linkoping, Sweden, ISSN <nobr style="background-color: rgb(255, 241, 184); color: blue; cursor: pointer; border-radius: 3px; border: 1px solid rgb(170, 170, 170)" title="sipgate Click2Dial for <nobr style="background-color: rgb(255, 241, 184); color: blue; cursor: pointer; border-radius: 3px; border: 1px solid rgb(170, 170, 170)" title="sipgate Click2Dial for 03784738" sipgateffx_number="03784738">03784738chrome://sipgateffx/skin/icon_click2dial.gif</nobr>" sipgateffx_number="0378-4738 ">0378-4738 chrome://sipgateffx/skin/icon_click2dial.gif</nobr>= Water SA Vol. 24 No. 2 April 1998.
Joseph, J. 2005. “The Humanure Handbook”,A guide to Composting Human Manure, Third Edition ISBN-13: 978-0-9644258-3-5, ISBN-10: 0-9644258-3-1, Published by Joseph Jenkins, Inc. PO Box 607, Grove City, PA 16127 USA.
Lutz, W., & Samir, K. C. (2010). Dimensions of global population projections: what do we know about future population trends and structures? Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 365(1554), 2779–91. doi:10.1098/rstb.2010.0133.
Soe, K. Z. A. 2012. “Struggle with Uncertainties: Livelihood of the Intha in Inle Lake of Myanmar”, ICIRD (International Conference on International Relations and Development) 2012, pdf.
Morgen, P.2007.“Toilets that make compost, Low cost, Sanitary toilets that produce valuable compost for crops in an African Context”, Stockholm Environment Institute, EcoSanRes Programme, 2007. www.econsanres.org, www.sei.se.
United Nation-WCED, 1987. "Our Common Future, A report published by the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED)”, UN Documents: Gathering a Body of Global Agreements has been compiled by the NGO Committee on Education of the Conference of NGOs from United Nations web sites with the invaluable help of information & communications technology. in 1987.
Schutte, C.F and Pretorius, W.A (1997). “Water demand and population growth”. Water SA (23) <nobr style="background-color: rgb(255, 241, 184); color: blue; cursor: pointer; border-radius: 3px; border: 1px solid rgb(170, 170, 170)" title="sipgate Click2Dial for <nobr style="background-color: rgb(255, 241, 184); color: blue; cursor: pointer; border-radius: 3px; border: 1px solid rgb(170, 170, 170)" title="sipgate Click2Dial for (2)127134 (Morocco)" sipgateffx_number="(2)127134 ">(2)127134 chrome://sipgateffx/skin/icon_click2dial.gif</nobr>(Morocco)" sipgateffx_number="(2) 127-134">(2) 127-134chrome://sipgateffx/skin/icon_click2dial.gif</nobr>.
Swe, K.L, 2011. “Development of Clean Water and Sanitation in Inle Lake, Myanmar”, EE2 seminar: Water and Environment In Asia’s Developing Communities Singapore International Water Week 2011 Co-located Event, Organized by the Lien Foundation- Nanyang Technological University, Environmental Endeavour (EE2), 6-july-2011.
VITO (Vision on Technology), 2012. “Transition in Research, Research In Transition-When technology meets sustainability”, Vito series-1, Responsible Publisher: Dirk Fransaer, Boeretang 200, 2400 MOL, Belgium @ 2012 VITO NV www.vito.be.
World Bank Report, 2012.“Turn Down the Heat, why a 4 .C warmer world must be avoided”, A report for the world bank by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and Climate Analytics, November, 2012.
World scientists’ warning to Humanity, signed by 1600 senior scientists from 70 countries including 102 Nobel Prize laureates, November 18, 1992.
Further Readings
Education and Sanitation on Pollution Management:
http://www.buildinggreen.com/features/mr/waste.cfm
Composting Toilet By “Composting toilet” Ping, F.C, Afshar, S. H, and Klang, A. 2011. “Composting toilet”, Feb, 2011, pdf. http://www.envirolet.com/enlowwatrems6.html
Composting Toilet Technology in Urban Apartments & Agricultural Trials, Salmon et al.. 2003. pdf
Salmon.pdf Composting toilet Technology in Urban Apartment,
Design Review of Composting Toilet and Composting Method; Design Review of Composting Toilet and Composting Method